Tinnitus, often described as a constant ringing or buzzing in the ears, can be a frustrating experience. While many people associate tinnitus with issues related to the ears, fewer might consider the health of their teeth and gums as a contributing factor. Yet, recent studies suggest a connection between dental health and the occurrence of tinnitus.
The structures of the mouth and jaw are closely connected to the ears. Problems in one area can sometimes lead to issues in another. For instance, stress on the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which hinges your lower jaw to your skull, can lead to ear problems including tinnitus.
Understanding this connection can open new doors for managing and possibly alleviating tinnitus. We'll dive into how your daily oral care routine might just be affecting what you hear, and share some practical advice on how to take care of both your ears and your mouth.
- What is Tinnitus?
- How Dental Health Impacts Hearing
- The Role of TMJ in Tinnitus
- Real-Life Case Studies
- Tips for Better Oral and Ear Health
- When to See a Specialist
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a condition where individuals perceive a ringing, buzzing, hissing, or even chirping sound in their ears without an external source. This sound can vary in pitch and intensity, sometimes becoming loud enough to interfere with daily activities and sleep. It’s estimated that nearly 15-20% of people around the world experience some form of tinnitus, making it a relatively common issue.
The exact cause of tinnitus isn't always clear. Often, it’s related to hearing loss, which can be due to age, exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or earwax build-up. However, other factors such as stress, head and neck injuries, and certain medications can also trigger or worsen the condition. An interesting fact is that some people with tinnitus can even experience it in rhythm with their heartbeat (a condition known as pulsatile tinnitus).
There are two primary types of tinnitus: subjective and objective. Subjective tinnitus is the most common and is only heard by the affected person. Objective tinnitus, on the other hand, can be heard by a doctor during an examination and is often caused by vascular or muscular issues. Though tinnitus is usually considered a symptom rather than a standalone condition, the persistent noise can lead to significant distress, impacting both mental and physical well-being.
As Dr. Charles Limb, a leading researcher in the field, says, “Tinnitus may be the result of the brain’s efforts to fill in missing auditory input. Think of it as the brain’s way of compensating for a lack of sound signals.”
Researchers are continually looking for new ways to understand and treat tinnitus. One key area of study involves the brain’s auditory pathways and how they process sound. Tools like MRIs and CT scans have shown that changes in these pathways can contribute to tinnitus. For some, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help manage the emotional and psychological impact of the constant noise. Other treatments include sound therapy, medication, and even lifestyle changes to reduce stress and improve sleep.
It's important to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience persistent tinnitus. They can help determine the underlying cause and suggest appropriate treatment options. While there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, a combination of treatments tailored to individual needs often brings the best results. So, if you find yourself dealing with tinnitus, know that you're not alone and there are ways to manage it effectively.
How Dental Health Impacts Hearing
Dental health and hearing might seem like unrelated aspects of wellness, but they are more interconnected than you might think. One primary way they influence each other is through the location and function of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). This joint, which connects your jawbone to your skull, sits right next to your ear canal. When there is stress or inflammation in this joint, it can affect your hearing and potentially lead to tinnitus.
Issues like improper bite alignment or bruxism (nighttime teeth grinding) can put added stress on the TMJ. This strain can then cause a chain reaction that leads to muscle tension and even inflammation, which could affect the nerves and blood vessels near the ear. As a result, you might experience symptoms like ringing, buzzing, or other noises, which are characteristics of tinnitus.
Another link between dental health and tinnitus comes from infections or abscesses in the mouth and gums. Poor oral hygiene can lead to bacterial infections which might spread and reach the ear, potentially causing both pain and auditory disturbances. Moreover, some dental procedures themselves can temporarily affect hearing. For example, if you’ve had extensive dental work, especially on the lower jaw, you might notice a temporary onset of tinnitus.
Interestingly, scientific studies have explored this relationship. According to research published in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, around 50% of patients with TMJ disorders also reported experiencing some form of tinnitus. This data indicates a strong correlation that shouldn’t be overlooked. If you’re facing unexplained ringing in your ears and also have dental issues, consulting both a dentist and an audiologist might be a prudent step.
“The association between temporomandibular joint disorder and tinnitus is particularly significant. Patients often find relief from ear-related symptoms after addressing their dental health.” — Dr. Alex Greenfield, a leading TMJ specialist
Furthermore, dental health problems can indirectly affect your overall well-being, impacting your stress and anxiety levels, which are known triggers for tinnitus. Maintaining good oral hygiene is a step towards mitigating these risks. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can go a long way in preventing these issues.
In conclusion, your mouth and ears share more than just proximity; their health conditions are intimately linked. By taking care of your dental health, you may also find improvements in your ear health, thereby reducing the symptoms of tinnitus. If you’re dealing with persistent ringing in your ears and haven't explored potential dental causes, it might be worth mentioning to your healthcare providers.

The Role of TMJ in Tinnitus
The temporomandibular joint, or TMJ, serves a crucial function in your daily life. It enables the movements required for talking, chewing, and yawning. This joint connects your lower jawbone to your skull and is located in front of your ears. Problems with the TMJ can lead to discomfort, including headaches, jaw pain, and notably, tinnitus. The proximity of the TMJ to the ears means that issues in this joint can easily be referred to the ears, manifesting as that persistent ringing or buzzing sound known as tinnitus.
It's fascinating how interconnected our body systems are. When the TMJ is misaligned or if the muscles around it are tense and strained, it can put pressure on the auditory system. For instance, the tiny muscles and nerves around the TMJ also extend to the ear. When these muscles become fatigued or overworked, it can impact the inner workings of your ear, potentially triggering tinnitus symptoms. Often, people with TMJ disorders also exhibit ear symptoms like a feeling of fullness, ear pain, and tinnitus.
Dr. Susan Shore, a professor of otolaryngology at the University of Michigan, states,
"TMJ disorder is often overlooked in cases of chronic tinnitus, yet it plays a significant role in the quality of life for these patients."This is why understanding the connection between the TMJ and tinnitus is vital. Recognizing TMJ symptoms early and addressing them can often provide relief from tinnitus. Common symptoms of TMJ disorders include clicking or popping sounds when opening and closing the mouth, limited jaw movement, and frequent headaches. If you experience any of these alongside tinnitus, paying attention to your jaw health might be beneficial.
Managing TMJ-related tinnitus often involves several approaches. Physical therapy can be effective in easing muscle tension and improving jaw alignment. Exercises designed to strengthen and stretch the jaw muscles can provide significant relief. Additionally, using heat or cold packs, practicing stress management techniques, and maintaining good posture can also help alleviate symptoms. In some cases, dental interventions like bite adjustments or the use of mouth guards can correct misalignment issues, potentially easing tinnitus.
Another essential aspect to consider is diet. Foods that are hard to chew can exacerbate TMJ issues because they require more effort from the jaw muscles. Softening your dietary choices can sometimes reduce strain on the TMJ and help with associated ear symptoms. Moreover, avoiding habits like gum chewing or nail biting can prevent unnecessary stress on the jaw joint. Being mindful of how you use your jaw during daily activities can go a long way in reducing symptoms.
If home remedies and lifestyle changes are not enough to relieve TMJ and associated tinnitus, it may be time to seek professional help. Specialists such as dentists who focus on TMJ disorders or otolaryngologists (ear, nose, and throat doctors) can offer tailored treatments. They might use imaging tests to get a better look at your jaw and ear structures or recommend specific treatments like corticosteroid injections or even surgery in severe cases. The goal is to provide a comprehensive approach to relieve both TMJ disorder and its secondary symptoms, including tinnitus.
Understanding the role of the TMJ in tinnitus is a breakthrough for many patients who have struggled with ear ringing without a clear cause. By addressing TMJ disorders and implementing targeted treatments, there is a significant chance of alleviating tinnitus symptoms. If you've been dealing with both jaw and ear issues, considering the TMJ's role could be the first step towards a solution. Remember, taking action early can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Real-Life Case Studies
Sometimes, seeing how an issue affects real people makes a complicated topic more relatable. Let’s dive into some real-life case studies where dental health had a surprising impact on tinnitus.
Take Maria, a 45-year-old graphic designer from New York. She had been struggling with tinnitus for several years. The ringing in her ears was often so loud that it interfered with her work and sleep. Despite trying different treatments, including medication and behavioral therapy, nothing seemed to help. Finally, on a recommendation from a friend, she decided to see a dentist who specialized in temporomandibular joint disorders.
The dentist discovered that Maria had a misaligned bite, putting pressure on her TMJ. After undergoing treatment to correct her bite, Maria noticed a significant reduction in her tinnitus symptoms. The buzzing wasn't gone entirely, but it was manageable enough that she could focus on her work again.
Another compelling story is that of John, a 56-year-old contractor from Kansas. John didn't only suffer from tinnitus but also had frequent migraines. During a routine dental check-up, his dentist observed that John had several worn-down teeth, likely from grinding them in his sleep. He was fitted with a night guard to protect his teeth and ease the stress on his jaw.
Within just a few weeks of using the night guard, John reported fewer headaches and a noticeable decrease in the intensity of his tinnitus. John’s case suggests that sometimes simple changes in managing dental health can have far-reaching benefits, especially for symptoms not initially related to oral issues.
"A well-aligned jaw can be the key to relieving pressure on the ears," says Dr. Linda Smith, a prominent TMJ specialist.
Yet another case involves Emily, a young college student from California. Emily had persistent tinnitus that made concentrating in class incredibly difficult. Her dentist noticed signs of gum disease and advised a more rigorous oral hygiene routine. Surprisingly, as her gum health improved, Emily found her tinnitus becoming less intrusive.
These stories point to the interconnectedness of our bodies, showing how different aspects of health can influence each other in unexpected ways. If you’re experiencing tinnitus, it’s worth exploring whether your dental health might be a contributing factor.
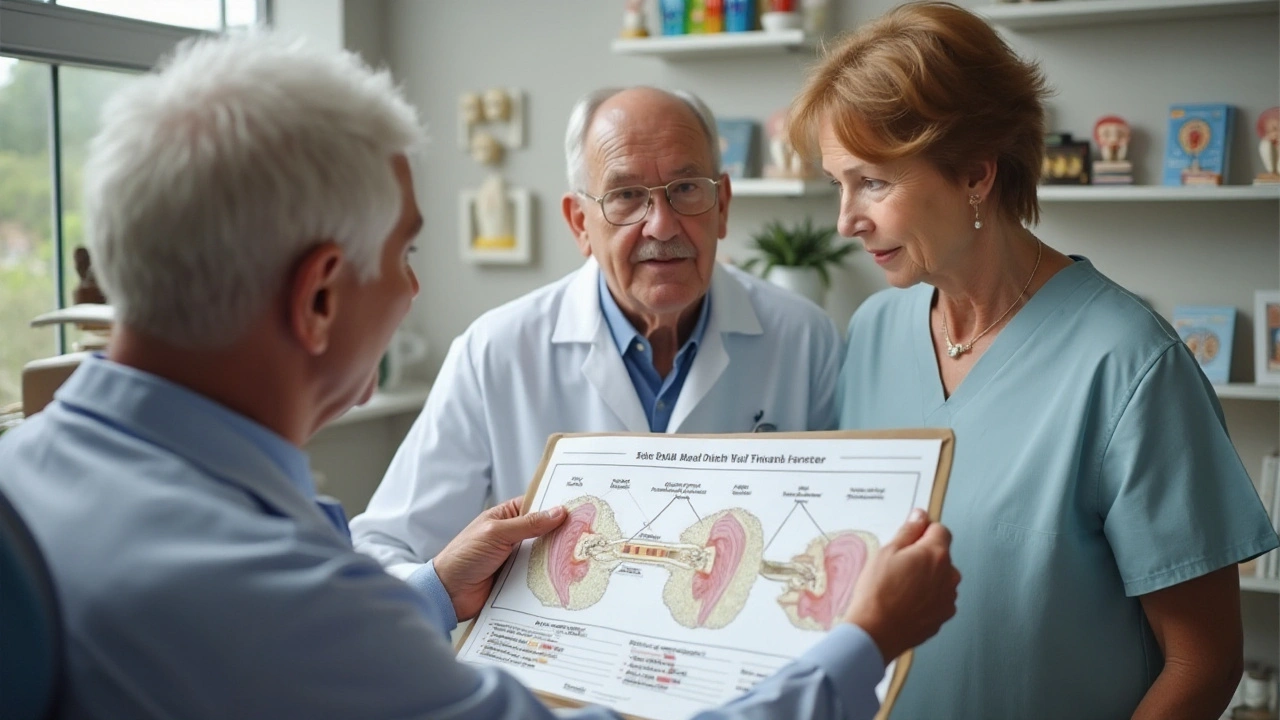
Tips for Better Oral and Ear Health
Maintaining optimal dental health is not just about a sparkling smile; it could also be a hidden key to reducing issues like tinnitus. One of the first steps is to adopt a rigorous oral hygiene routine. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste can significantly reduce the risk of oral infections, which may have a cascading effect on ear health. Don't forget to floss daily, as it helps remove the plaque and food particles that a toothbrush can't reach, further lowering your chances of oral health issues that could potentially affect your ears.
"Good oral health habits have a direct impact on overall well-being, including aspects you might not initially consider, like hearing," says Dr. Michelle Collins, a renowned dentist specializing in oral-systemic health.
Regular visits to your dentist are equally essential. Professional cleanings and check-ups can catch issues like gum disease and cavities early on. Ignoring dental problems can lead to more serious conditions that might indirectly cause or worsen tinnitus. During your visits, mention any ear-related symptoms you're experiencing. Your dentist might offer insights or refer you to a specialist.
Proper alignment of your teeth also plays a crucial role. Misaligned teeth can cause stress on your temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which is closely connected to the ears. If you're experiencing jaw pain or clicking sounds when you chew, these could be signs of TMJ disorders that might contribute to tinnitus. Orthodontic treatments like braces or Invisalign can help correct these issues, offering relief to both your mouth and ears.
Another aspect often overlooked is the impact of diet on dental and ear health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports healthy teeth and gums, potentially reducing the underlying causes of tinnitus. Foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds, strengthen your teeth. Meanwhile, foods rich in Vitamin D help your body absorb calcium, creating robust oral health that benefits your overall well-being.
Stress management is vital for both oral care and ear health. High stress levels can exacerbate teeth grinding, leading to TMJ problems and subsequently tinnitus. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can be beneficial. Consider using a mouthguard at night if you grind your teeth while sleeping.
If you use dental appliances like dentures or mouthguards, make sure they fit properly. Ill-fitting appliances can lead to discomfort and even oral health issues, contributing to a cascade of problems including tinnitus. Always consult with your dentist to ensure your dental appliances are in good condition and fit well.
Lastly, avoid habits that harm your dental health. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to gum disease, tooth decay, and even damage to your auditory system. Cutting back on these habits can improve both your dental and ear health in the long term. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, as it helps wash away food particles and bacteria, promoting a healthier mouth and potentially reducing the risk of tinnitus.
When to See a Specialist
It’s crucial to know when to seek help from a specialist if you’re grappling with tinnitus, especially if your efforts at home aren’t providing relief. The first step is recognizing that the persistent ringing in your ears isn’t something you have to live with. If the ringing gets louder or more frequent, it's a good idea to get a professional opinion. For people who experience tinnitus along with significant dental issues, visiting a dentist with knowledge about TMJ disorders might be a wise move.
If your tinnitus comes and goes or happens after you’ve been grinding your teeth or clenching your jaw, it’s another sign that a specialist should be consulted. There are also cases where tinnitus is accompanied by symptoms like dizziness, sudden hearing loss, or pain in your jaw and face. Pain that extends from your jaw into your ears can be a sign of a TMJ disorder, and it’s something a specialist can diagnose and treat more effectively.
A specialist can provide targeted tests to better understand the underlying causes of your tinnitus. For example, they might recommend imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan to check the jaw or ear structures. They might also suggest blood tests to rule out other potential health conditions. Understanding the specific cause of your symptoms can guide a more effective treatment plan. A specialist can also make you aware of the connections between ear ringing and oral health that aren't widely known even among many general practitioners.
For those who have already tried various treatments without success, seeking a specialist’s expertise gives you access to options like cognitive behavioral therapy or sound therapy tailored specifically to tinnitus. Some specialists might recommend devices that generate low-level noise to help mask the tinnitus sounds, making your life more comfortable.
As Dr. Jane Lewis, an audiologist with over 20 years of experience, mentions, "Early intervention by a specialist can make a significant difference in managing tinnitus effectively."
It’s also important to mention that seeing a specialist isn't just about treating the symptoms but also about preventing further complications. Regular check-ups can ensure that any dental issues contributing to tinnitus are kept under control. This makes consulting a specialist a proactive step towards better long-term health, as opposed to a reactive one after the situation has worsened substantially.
In some cases, a multidisciplinary approach might be the best way to manage the issue. This means your dentist might refer you to an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist or an audiologist for a comprehensive treatment plan. Combining expertise from different fields ensures that both your dental health and ear health are addressed thoroughly, which can significantly improve your quality of life.
Ultimately, knowing when to seek professional help can save you from unnecessary suffering. Don’t wait until your symptoms disrupt your daily activities or mental well-being before you take action. Remember, addressing both your dental health and tinnitus with the guidance of specialists can lead to more effective and lasting solutions.




America's dentnal care is on the brink, and that ringing in ears is just another symptom of our failing health system.
September 20Mark Haycox